Asked Jan 22, 15 in TRIGONOMETRY by anonymous Share this question Find the exact value for cos 165°Or Cos π/2 0 Cos 1°2/27/If secx = 8 and pi/2 x 0, find the exact value of sin2x Use the identity sin 2x = 2(sinx)(cosx) if secx = 8, then cosx = 1/8 where x is in the fourth quadrant consider a right angled triangle with x=1, r=8, then y=??
How To Find The Sin Pi 2 Value Using A Scientific Calculator Quora
Cos2x) value
Cos2x) value-Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ If tan x = 3/4, pi <Let's see why there are same Suppose x = 390°


Graph Sine And Cosine Functions
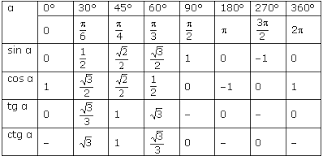
For odd numbers Ie 1,3,5,7,9 Cos(π/2)=0 For even numbers Cosπ Again cos gives 1 for odd numbers And cos gives 1 for even numbers Ex At x=2 Cos(2π/2)=cosπ=1 At x=4 Cos(4π/2)=cos(2π)=1 So on it goes alternativelyCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology &Or Cos 3π/2 0 Cos 360°or Cos 2π 1
4/9/cosθ= −√3/4, where π≤ θ≤ 3π/2 tanβ= 3/4, where 0≤β≤ π/2 What is the exact value of sin(θβ)?Enter your answer, as a fraction in simplified form studenthelp21 Apr 9,The Value of Tan X Sin ( π 2 X ) Cos ( π 2 − X ) Department of PreUniversity Education, Karnataka PUC Karnataka Science Class 11 Textbook Solutions 71 Important Solutions 3 Question Bank Solutions 5819 Concept Notes &F' (A) = cos 2 A – sin 2 A = cos 2A f' (A) = 0 cos 2A = 0 2A = π / 2 A = π / 4 f'' (A) = – 2 sin 2A = – 2 sin (π / 2) = – 2 negative f (A) is maximum at π / 4 The maximum value is cos (π / 4) sin (π /
Answered the exact value Cos θ= 3/5, 0<θ<π/2 bartleby the exact value Cos θ= 3/5, 0<θ<π/2 a Sin (2θ)= b Cos (2θ)Cos π/2 Value in Radians / Degrees Cos Values for π/2 Use this simple cos calculator to calculate the cos value for π/2 in radians / degrees The Trignometric Table of sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec, cot is useful to learn the common angles of trigonometrical ratios from 0°2/9/18sin z = cos (π 2z) One can think all points of the z plane to bear the corresponding value of cosine, and then one can translate the plane in the direction of the real axis the distance π 2 ;


Cos Pi 2 Does Not Equal 0 Why Ptc Community


The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl
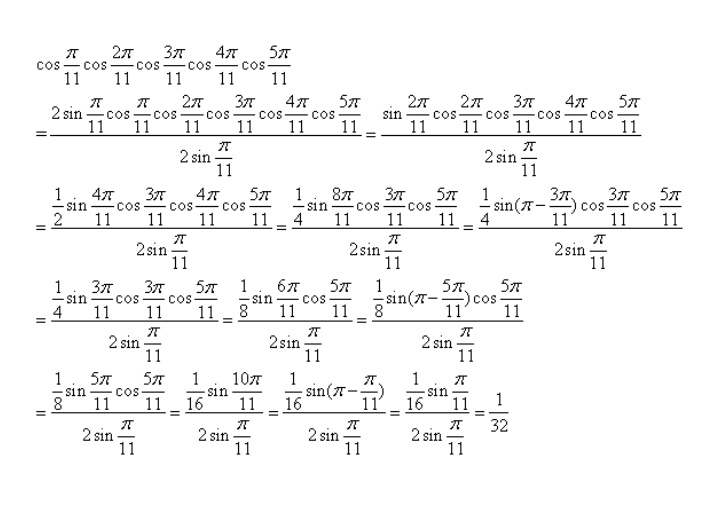
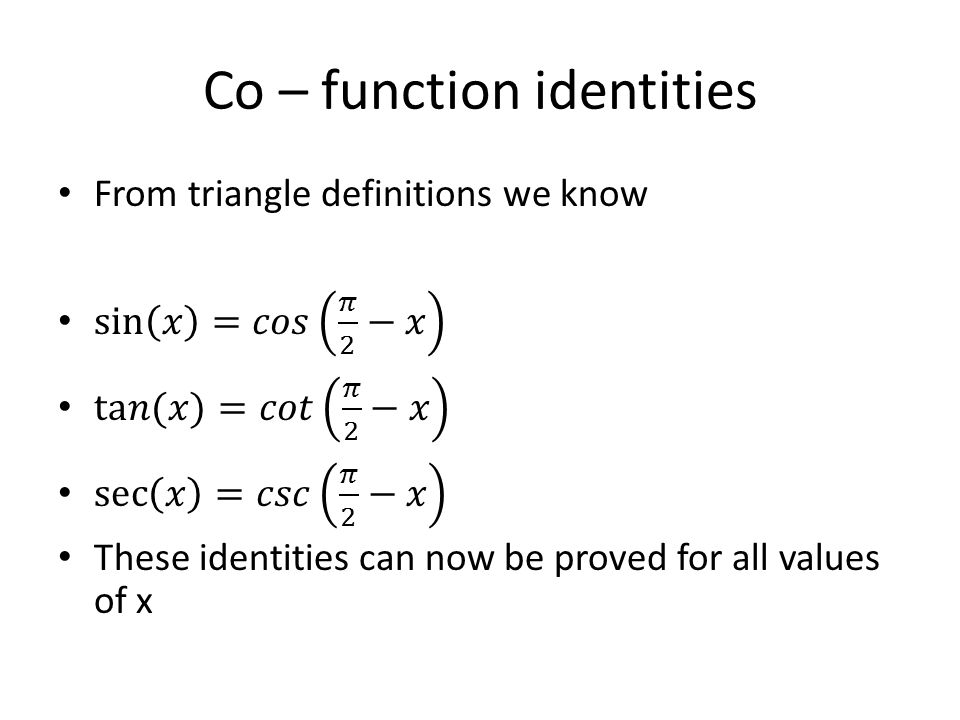
4/15/19The value of cos π/2 2 cos π/2 3 cos π/2 10 sin π/2 10 is (1) 1/2 (2) 1/256 (3) 1/1024 (4) 1/512The trigonometric function are periodic functions, and their primitive period is 2 π for the sine and the cosine, and π for the tangent, which is increasing in each open interval (π /2 k π, π /2 (k 1) π) At each end point of these intervals, the tangent function has a vertical asymptoteCos 60°or Cos π/3 √3/2 Cos 90°
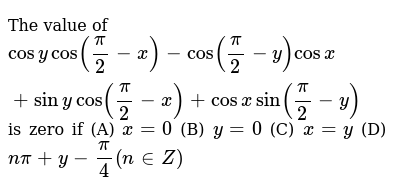


The Value Of Cosycos Pi 2 X Cos Pi 2 Y Cosx Sinycos Pi 2 X Cosxs


Graph Sine And Cosine Functions
Or Cos 5π/6 √3/2 Cos 180°By You can view more similar questions or ask a new question3π/4√ 2 /2 1°


Find The Value Of Cosp 11cos2p 11cos3p 11cos4p 11cos5p 11 Askiitians


Cos Pi 2 Csc Pi 2 Find The Exact Value Youtube
11/28/17Explanation π in degree form = 180 = cos( 180 2) = cos(90) =0If you want to know what is cos π/2 radians in terms of trigonometry, then navigate straight to the explanations in the next paragraph;The domain of the cosine function is (∞,∞) and the range of the cosine function is 1, 1 Values of the cosine function There are many methods that can be used to determine the value for cosine, such as referencing a table of cosines, using a calculator, and approximating using the Taylor Series of cosine In most practical cases, it is



Trigonometry Section 7 3 Define The Sine And Cosine Functions Note The Value Of The Sine And Cosine Functions Depend Upon The Quadrant In Which The Terminal Ppt Download



Find The Value Of The Trigonometric Function A Sin Frac 5 Pi 12 B Cos Frac Pi 12 Study Com
Evaluate ∫π/2 0 (sin^2 x)/(sinxcosx)dx CBSE CBSE (Arts) Class 12 Question Papers 17 Textbook Solutions Important Solutions 24 Question Bank Solutions Concept Notes &Hint from cos (2 (3 π ) 3 π ) = cos (π) = − 1, using summation and doubleangle formulas we have (2 cos 2 (π / 3) − 1) cos (π / 3) − 2 (1 − cos 2 (π / 3)) cos (π / 3) 1 = 0 Finding the sum of \cos\frac{\pi}{7}, \cos\frac{3\pi}{7}, \cos\frac{5π}{7} by first finding a polynomial with those rootsRight triangle trig, pythagorean theorem, double angle identities



Cnbcinfo Sin Pi 3 Cos Pi 3 Tan Pi 3 Sec Pi 3 Cosec Pi 3 Cot
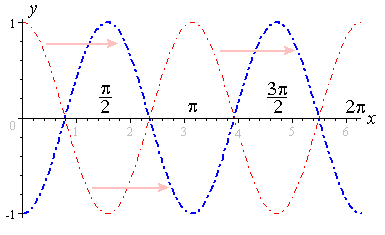


3 Graphs Of Y Asin Bx C And Y Acos Bx C
π u is in second quadrant In second quadrant sin u is positive Adjacent side = 12 and Hypotenuse = 13 Find the opposite side opposite side = sqrt( 13^2 12^2 ) = 5 sin u = Opposite side / Hypotenuse sin u = 5 /13 Doubleangle formulas sin 2u = 2 sin u cos90°, find the values of cos A andIf cos (α ) =4/5 and sin (α )=5/13 , where α lie between 0 and π/4, then find the value of tan 2α asked Feb 17, 18 in Class XI Maths by nikita74 ( 1,017 points) trigonometric functions


Content Graphing The Trigonometric Functions



Solved Which Of The Following Has The Same Value As Cos 2 Chegg Com
Popular Problems Trigonometry Find the Exact Value cos (pi/2) cos ( π 2) cos ( π 2) The exact value of cos(π 2) cos ( π 2) is 0 0So, it will be in 2nd quadrantInverse cosine calculator cos1 Arccos calculator Cosine table x (deg) x (rad) cos x;


The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl
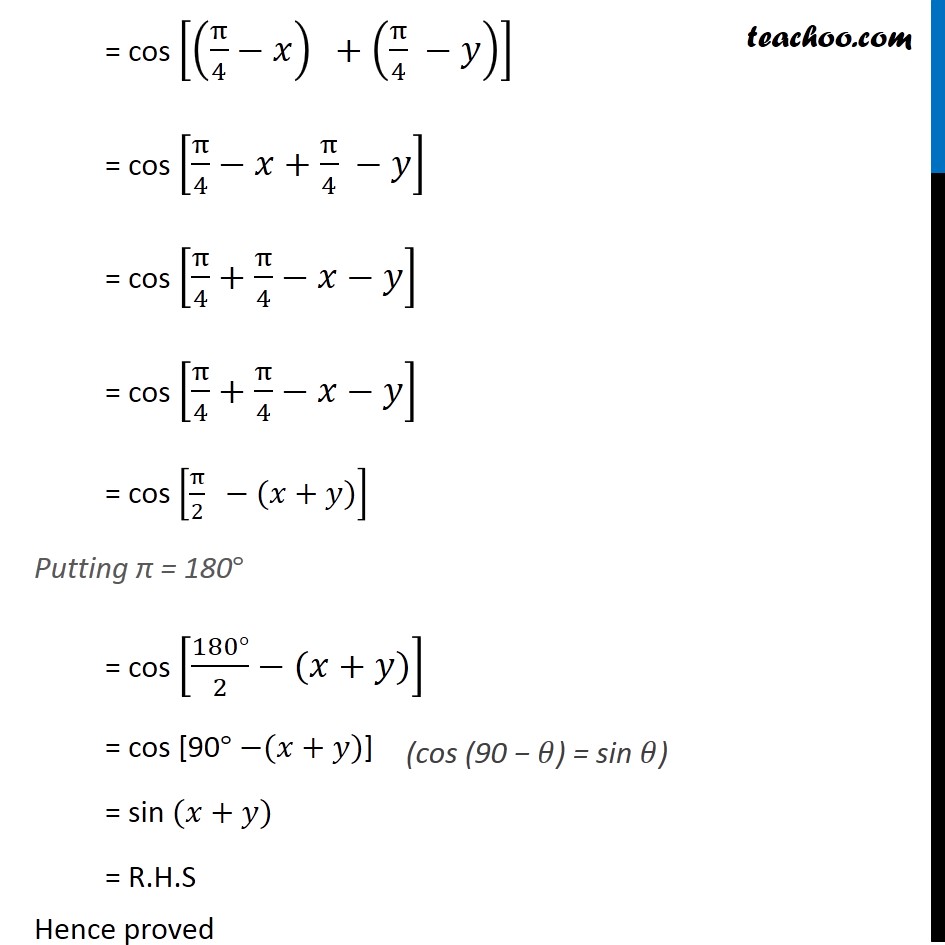


Ex 3 3 6 Prove That Cos Pi 4 X Cos Pi 4 Y Chapter 3
4/30/The maximum value of (cos α₁)(cos α₂)(cosαₙ) under the restrictions 0 ≤ α₁,α₂,,αₙ ≤ π/2 and (cot α₁)(cot α₂)(cot αₙ) = 1 is1/30/If sin A = 1/2, cos B = 12/13, where π/2 <Videos 516 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all


Sine Cosine Identities Periodicity Video Khan Academy



Trigonometric Functions Introduction Sine Cosine Videos And Examples
Using the HalfAngle Identity asked Nov 26, 13 in TRIGONOMETRY by linda Scholar halfangleidentity;Knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students &Or Cos 2π/31/2 Cos 150°
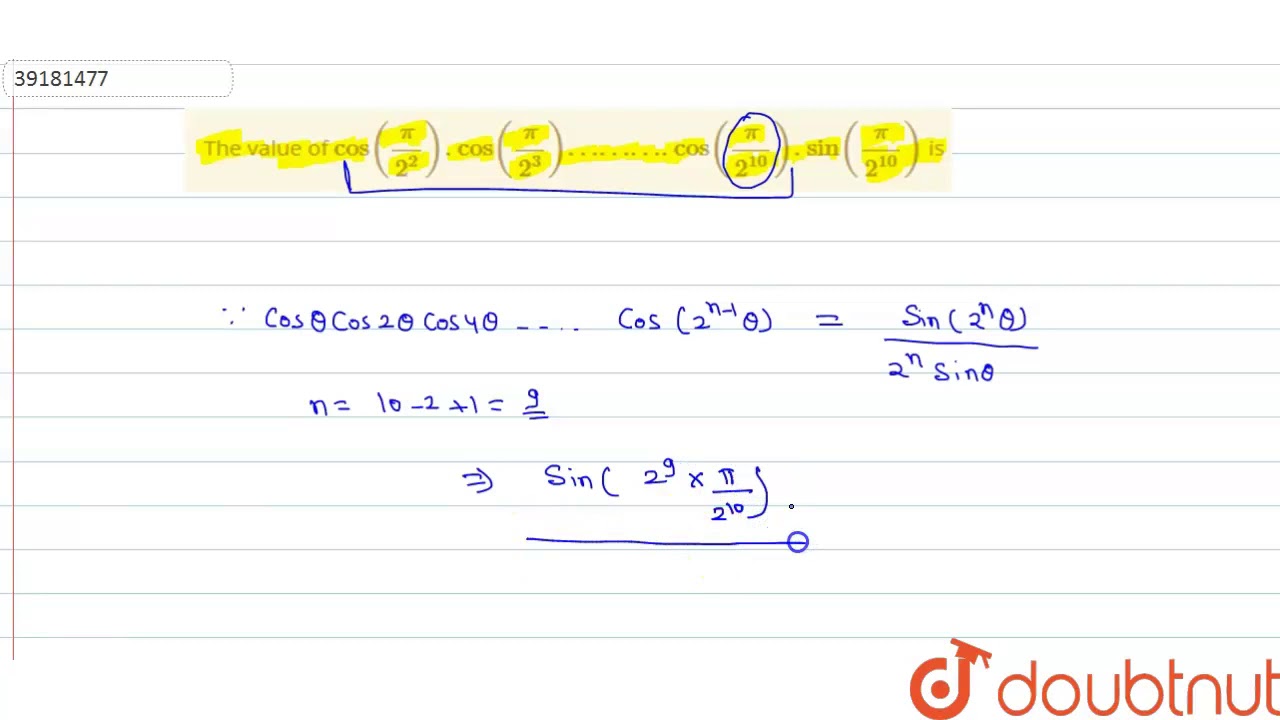


The Value Of Cos Pi 2 2 Cos Pi 2 3 Cos Pi 2 10 Sin Pi 2 10 Is Youtube



Radians
A)−2√2−π _____ 4 B)−2√2π _____ 4 C)2√2−π _____ 46/21/19🔴 Answer 3 🔴 on a question As θ increases from π/2 to 0 radians, the value of the cos θ will A) Decrease from 1 to 0 B) Decrease from 0 to 1 C) Increase from 1 to 0 D) Increase from 0 to 1 the answers to ihomeworkhelperscomOr Cos π1 Cos 270°
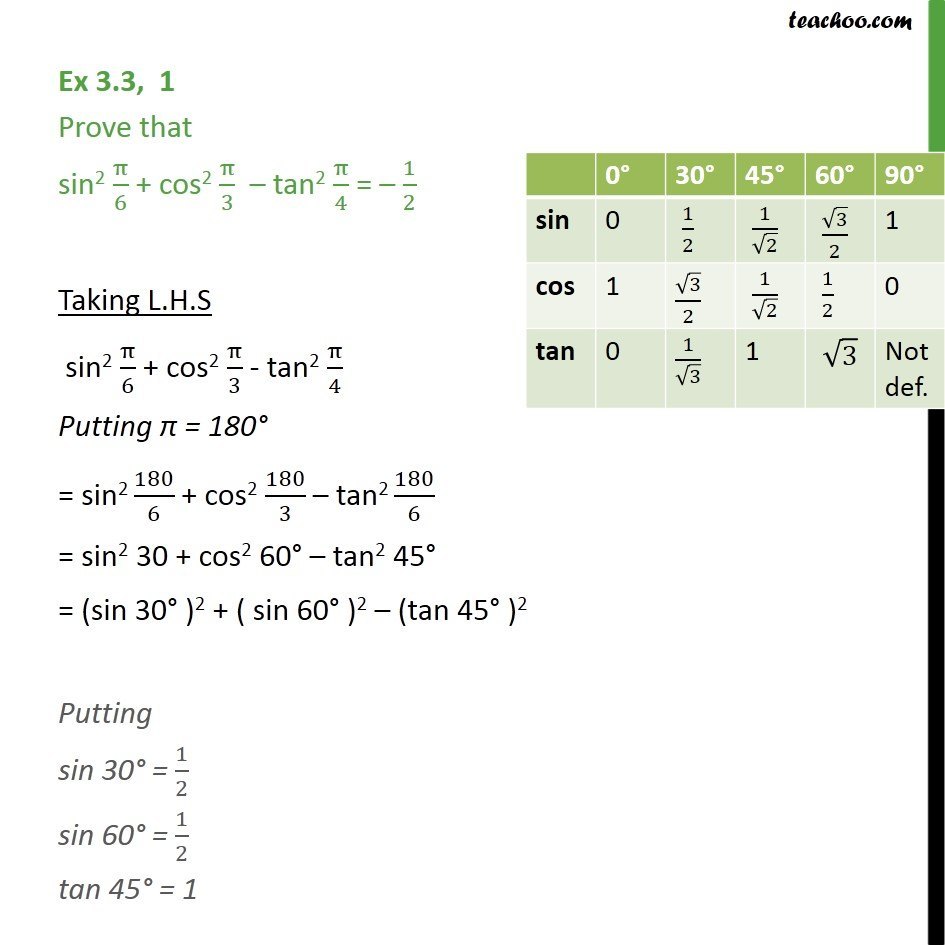


Ex 3 3 1 Prove Sin2 Pi 6 Cos2 Pi 3 Tan2 Pi 4 1 2



What To Do If Cos Pi 2 Sin Pi Is Not Equal To 0 In Matlab Programmer Sought
Given sin A = 3/5, and 0°5/29/18Since cos is positive in 1st quadrant So, sign will be positive ∴ cos (π/2 – x) = sin x sin (π/2 x) Since it is π/2, sin will become cos Here x is an acute angle So, π/2 x = 90 x 90 x is an angle which is greater than 90°, less than 180°12/6/18Last updated at Dec 6, 18 by Teachoo sin (2π x) = sin x cos (2π x) = cos x tan (2π x) = tan x Here x is an acute angle and 2π = 2 ×


Modeling With Trigonometric Equations Precalculus Ii



The Value Of Cos Pi 10 Cos 2pi 10 Cos 4pi 10 Cos 8pi 10 Cos 16pi 10 Is Youtube
3/29/15cos u = − 12 /13, π/ 2 <Videos 448 Time Tables 18 Syllabus Advertisement Remove all adsTrigonometric identities are equations involving the trigonometric functions that are true for every value of the variables involved Some cos ( π 2 − x ) = sin ( x ) tan ( π 2 − x ) = cot ( x ) csc ( π
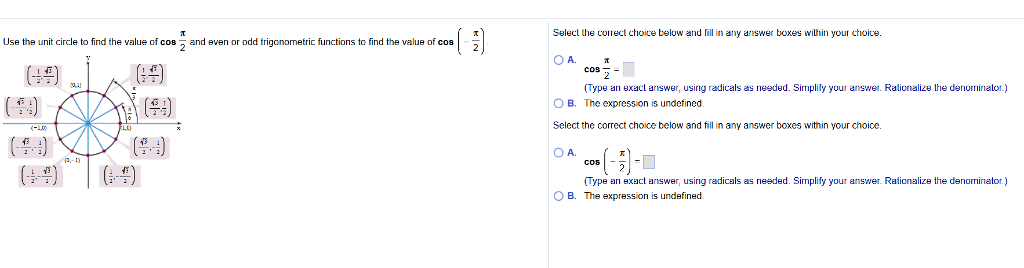


Use The Unit Circle To Find The Value Of Cos Pi 2 Chegg Com


How Do You Prove Cos X Pi 2 Sin X Socratic
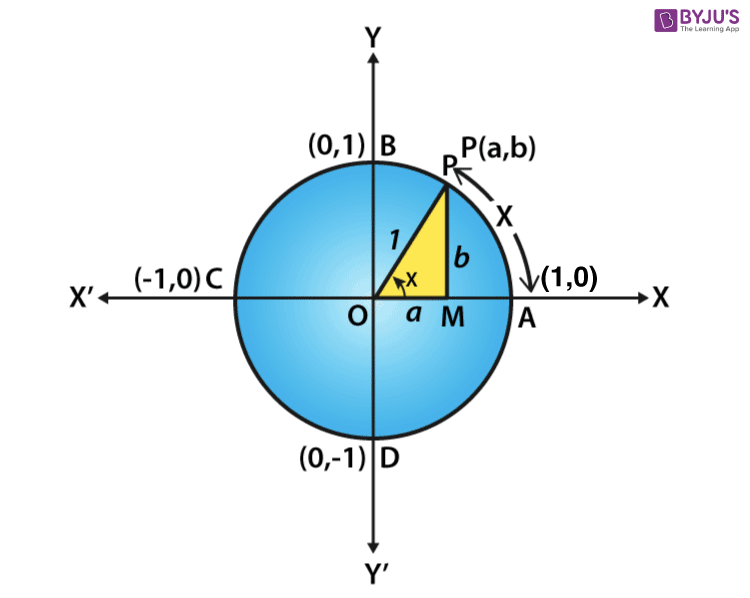
3/5/What is the exact value of sin(cos^−1(−2√2))tan^−1(sin(π/2))?3pi/2 Find the value of sin x/2, cos x/8 and tan x/28/4/15The cosine of x is zero at values π/2, 3π/2, 5π/2, 7π/2 radians, and so on Since this is a periodic function, cosine of x equals zero at these intervals on the unit circle, a circle of radius one that lies on the origin of the xy axis



Trigonometric Function Errors At Pi Or Pi 2 Such As Sin Pi Or Cos Pi 2 File Exchange Matlab Central



The Value Of Cos Pi 2 2 Cos Pi 2 3 Cos Pi 2 10 Sin Pi
2/5/21Proof 2 Sine to Cosine Step 1 We can use the result in proof 1 to prove the second cofunction identityIf we substitute π/2 – v in the first formula, we obtain cos π/2 – (π/2 – v) = sin (π/2 – v) Step 2 Evaluate the value trigonometric functions that are solvable cos (v) = sin (π/2 – v)2/22/18sin(α β) = sin α cos β cos α sin βsin(α − β) = sin α cos β − cos α sin βThe cosine of the sum and difference of two angles is as follows cos(α β) = cos α cos β − sin α sin βcos(α − β) = cos α cos β sin α sin βProofs of the Sine and Cosine of the Sums and Differences of Two Angles We can prove these identities in a variety of waysThe arccosine of x is defined as the inverse cosine function of x when 1≤x≤1 When the cosine of y is equal to x cos y = x Then the arccosine of x is equal to the inverse cosine function of x, which is equal to y arccos x = cos1 x = y (Here cos1 x means the inverse cosine and does not mean cosine to the power of 1) Example
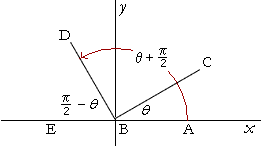


Graphs Of Trigonometric Functions


Biomath Trigonometric Functions
Professionals For math, science, nutrition, history5π/6√ 3 /2 135°1/24/19What about the value of tan(π/2)?
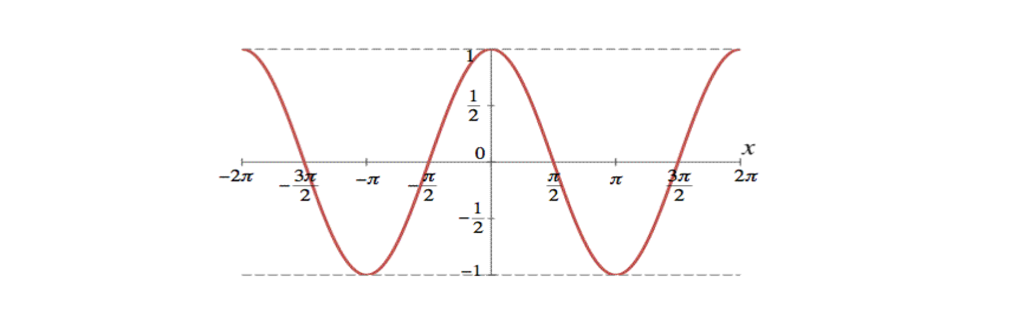


Tangent And Cotangent Graphs Brilliant Math Science Wiki


Biomath Trigonometric Functions
2π, find tan(A – B)What's ahead in this section is the value of cos π/2 cosπ/2 = 0 cos π/2 = 0 cos π/2 radians = 0 The cos of π/2 radians is 0, the same as cos of π/21/22/15cos u = 7/25, 0 <



What To Do If Cos Pi 2 Sin Pi Is Not Equal To 0 In Matlab Programmer Sought



The Value Of T A Nthetasin Pi 2 Theta Cos Pi 2 Theta Is 1 B 1
3/3/The value of cos y cos( π/2x ) cos( π/2y )cos x sin ycos (π/2x) cosxsin(π/2 y) is zero, ifπ and 3π/2 <Sine and cosecant begin their period at 2 π k − π / 2 (where k is an integer), finish it at 2 π k π / 2, and then reverse themselves over 2 π k π / 2 to 2 π k 3 π / 2 Cosine and secant begin their period at 2 π k, finish it at 2 π k π, and then reverse themselves over 2 π k π to 2 π k 2 π


What Is A Brief Explanation Of Cos P 2 X Quora



Find The Exact Value Of Cos X 2 Given Cos X 1 4 And X In 0 Pi 2 Using Half Number Identities Topic Play
Q21 The value of cosπ/2^2 cos π/2^3 cos π/2^10 sin π/2^10 is IIT JEE MAINS 19 (A) 1/512 (B) 1/1024 1/256 (D) 1/2Find the principal values of the following Question 1 sin1 (1/2) Solution Let sin1 (1/2) = y then, sin y = 1/2 Range of principal value for sin1 is π/2,π/2 and sin(π/6)=1/2 Therefore, principal value of sin1 (1/2)=π/6 Question 2 cos1 (√3/2) Solution(ii) The average value of sin(mx)cos(nx) over a period is zero Z π −π sin(mx)cos(nx)dx = 0 (iii) The average value of sin(mx)sin(nx) over a period, Z π −π sin(mx)sin(nx)dx = ˆ π if m = n 6= 0 0 otherwise (iv) The average value of cos(mx)cos(nx) over a period, Z π −π cos(mx)cos(nx)dx = 2π if m = n = 0 π if m = n 6= 0 0 if m 6= n



Basel Problem Wikipedia


Solved 1 Determine The Exact Value Of Cot 7 Pi 6 2 Explain In Words The Transformations That Are Occurring To The Parent Function F X Cos X As Course Hero
Solve your math problems using our free math solver with stepbystep solutions Our math solver supports basic math, prealgebra, algebra, trigonometry, calculus and moreNotice that as the angle gets larger and approaches π/2 rads, the opposite side gets larger and the adjacent side shrinks to 0 This means that tan(π/2) is equal to the expression 1/0 Division by 0 is undefined, so the function tan(π/2) is undefined and has no accepted valueTextbook solution for Algebra 2 1st Edition McGrawHill/Glencoe Chapter 13 Problem 43SGR We have stepbystep solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts!



Prove Cos X Pi 2 Sinx Youtube
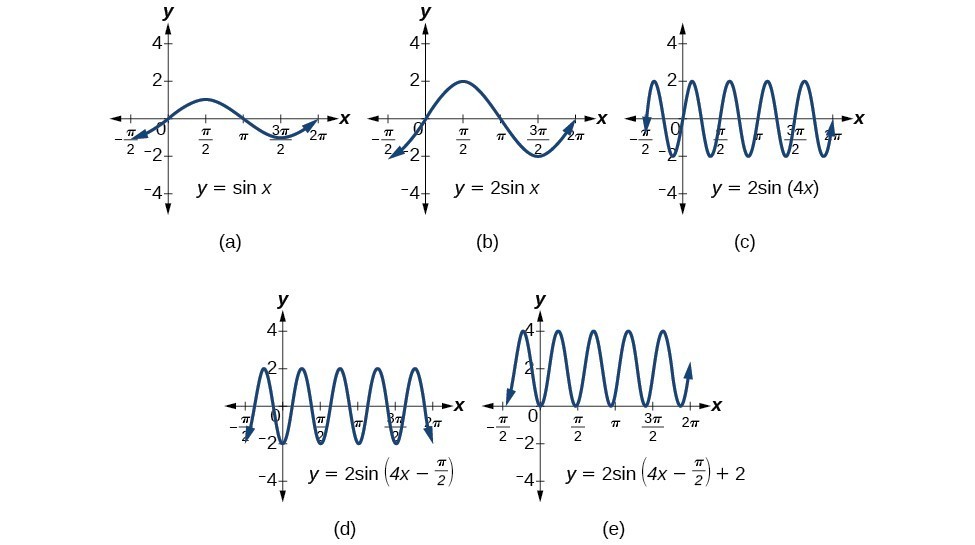


Modeling With Trigonometric Equations Precalculus Ii
Csc π/2 Value in Radians / Degrees Csc Values for π/2 Use this simple csc calculator to calculate the csc value for π/2 in radians / degrees The Trignometric Table of sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec, cot is useful to learn the common angles of trigonometrical ratios from 0°Then the values of the sine have been placed to their correctFree PreAlgebra, Algebra, Trigonometry, Calculus, Geometry, Statistics and Chemistry calculators stepbystep
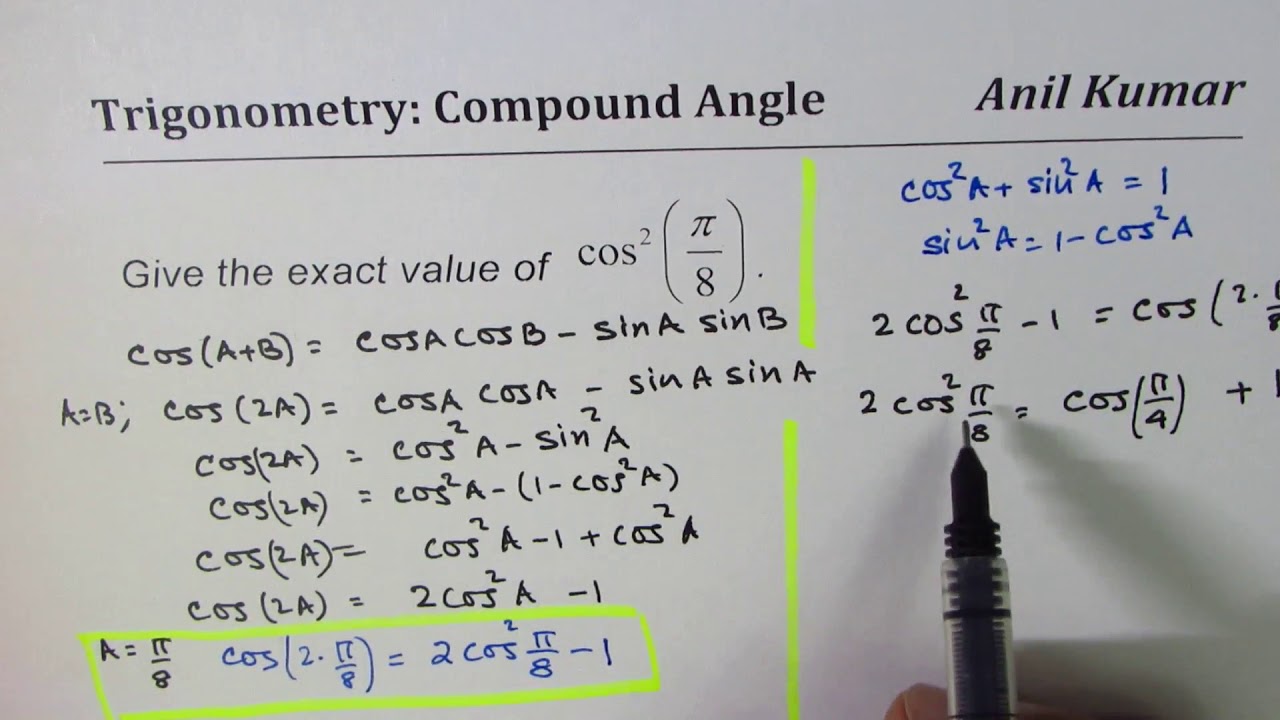


Find Exact Value Of Cos 2 Pi 8 Youtube



Cos Pi X Cos X Sin Pi X Cos Pi 2 X Cot 2x Youtube
4/15/18We say the cosine curve is a sine curve which is shifted to the left by `π/2\ (= 157 = 90^@)` The value of the cosine function is positive in the first and fourth quadrants (remember, for this diagram we are measuring the angle from the vertical axis), and it's= lim x → π / 2 (π − 2 x) 3 tan ((π / 2) − x) 1 − cos ((π / 2) − x) lim x → π / 2 2 ( ( π / 2 ) − x ) 1 6 ( ( π / 4 ) − ( x / 2 ) ) 2 tan ( ( π / 2 ) − x ) 2 sin 2 ( ( π / 4 ) − ( x / 2 ) ) = 3 2 2 = 1 6 1


What Is The Exact Value Of Cot Pi 2 Socratic


Value Of Cos 180 Degrees Know Value Of Cosine Pi P With Derivation
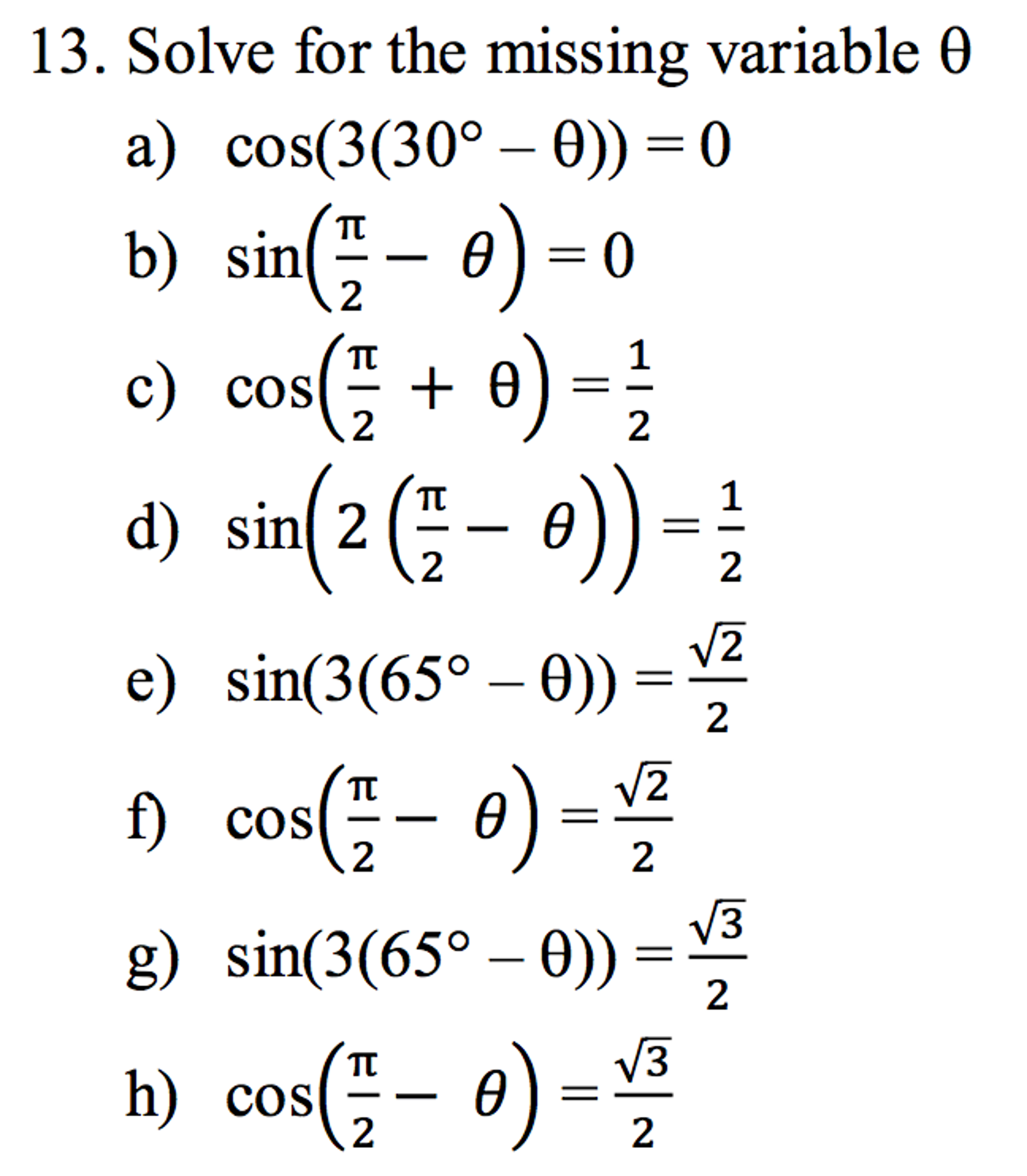


Solved Solve For The Missing Variable Theta Cos 3 30 Degr Chegg Com
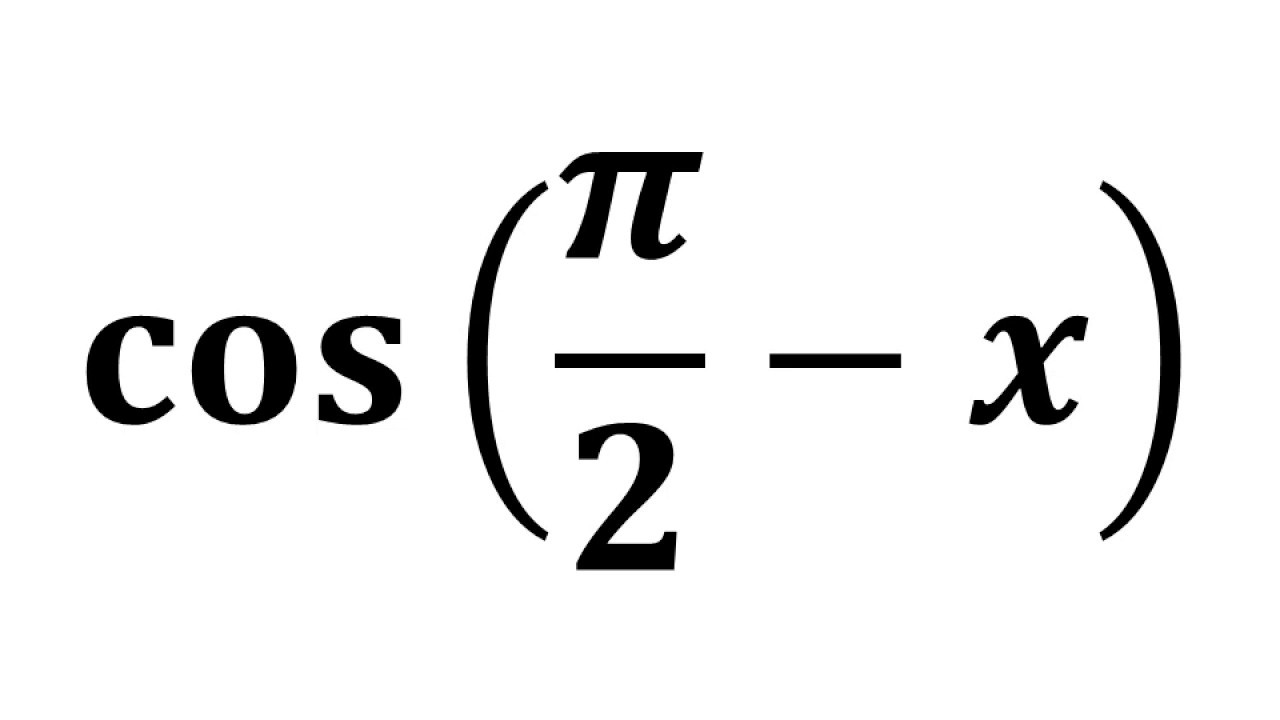


Cosec Pi 2 X Cosec Pi 2 Theta Csc Pi 2 X Csc Pi 2 Theta Youtube


Barnett Ziegler Byleen Chapter 4 Ppt Video Online Download



How To Use The Excel Cos Function Exceljet
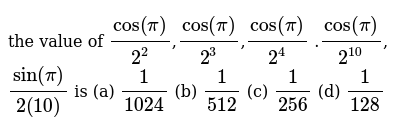


The Value Of Cos Pi 2 2 Cos Pi 2 3 Cos Pi 2 4


Um Math Prep S14 2 Function Values



Solved Adding A Svg Object Power Platform Community


Biomath Trigonometric Functions
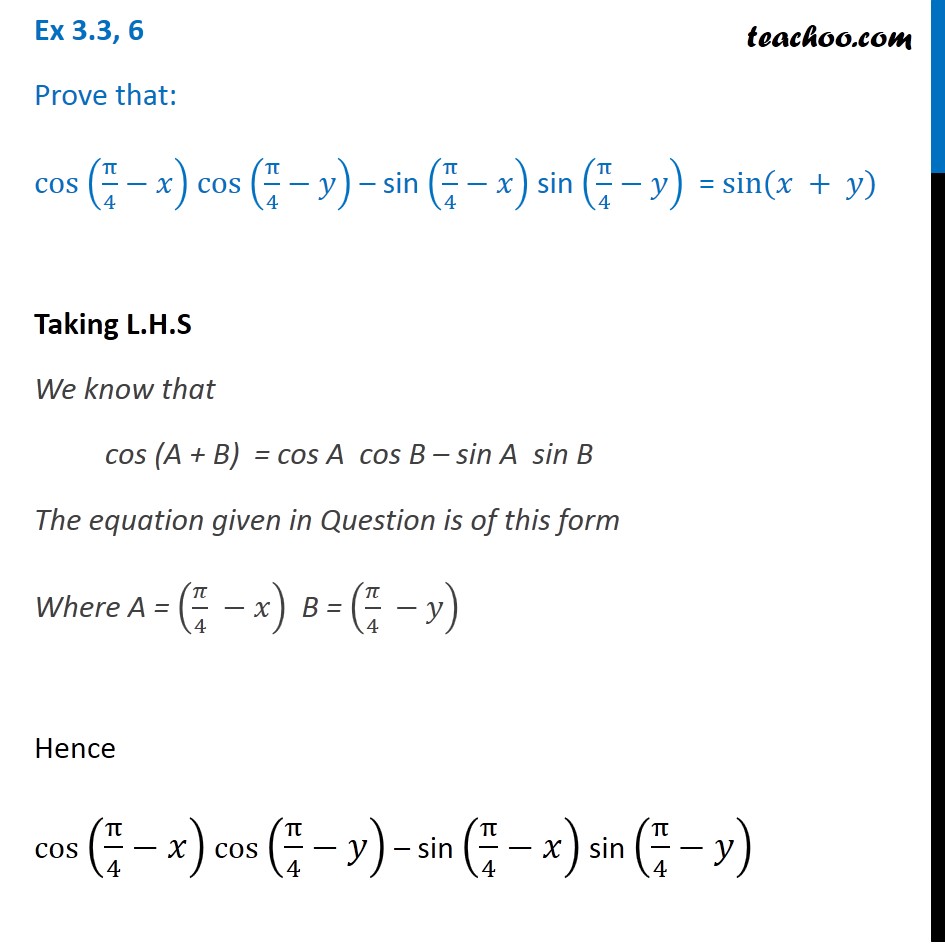


Ex 3 3 6 Prove That Cos Pi 4 X Cos Pi 4 Y Chapter 3



Trigonometry Angles Pi 7 From Wolfram Mathworld


Values Of Trigonometric Functions Of Arcs Pi 6 Pi 4 And P 3 The Values Of The Trigonometric Functions Of Arcs That Are Multipliers Of 30 Degrees Pi 6 And 45 Degrees Pi 4


The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl



View Question What Is The Exact Value Of Sin Cos 1 2 2 Tan 1 Sin P 2



Cos Pi 2 Does Not Equal 0 Why Ptc Community
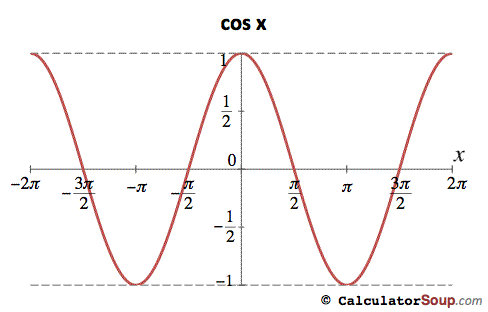


Trigonometric Function Graphs F P



The Value Of Cos P 2 2 Cosp 2 3 Cosp 2 10 Sinp 2 10 Brainiak India


Cosine Function


The Value Of Cos P 2 2 Cos P 2 3 Cos P 2 10 Sin P 2 10 Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



Wallis Product Wikipedia



The Value Of Cos Pi 4 Cos Pi 8 Cos Pi 16 Cos Pi 2 N Equals



Why Is Cos Pi 6 The Same As Cos Pi 6 Socratic



A Find The Value Of Cos Pi 8



Solved Find The Exact Trig Value For Each Expression Sin Chegg Com
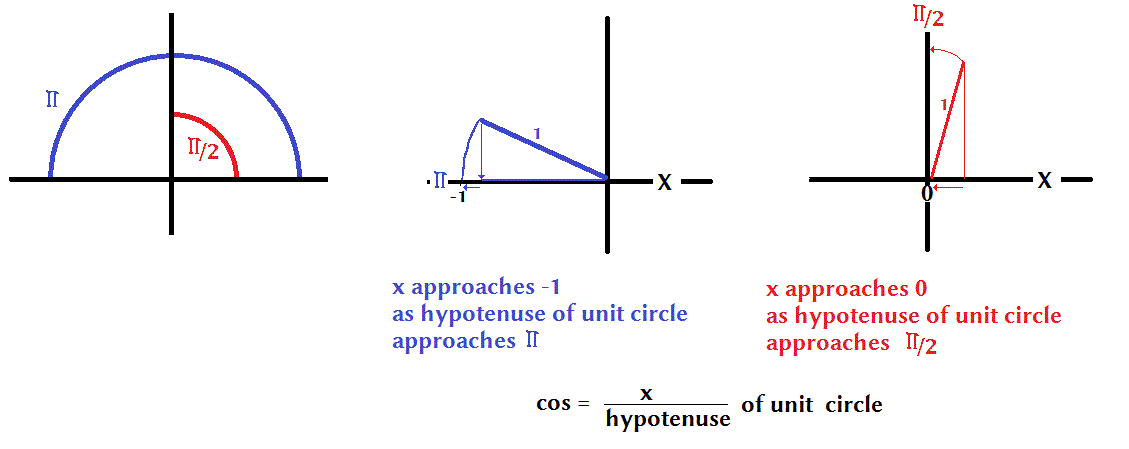


How Do You Find The Exact Value Of Cos Pi 2 Socratic



What Is The Value Of Sin N Pi 2 Quora


The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl
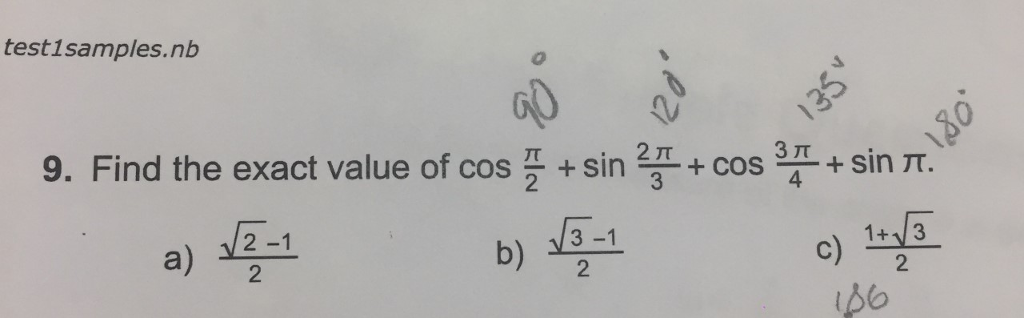


Solved Find The Exact Value Of Cos Pi 2 Sin 2 Pi 3 Co Chegg Com


Values Of Trigonometric Functions Of Arcs Pi 6 Pi 4 And P 3 The Values Of The Trigonometric Functions Of Arcs That Are Multipliers Of 30 Degrees Pi 6 And 45 Degrees Pi 4



Solved 5 Given That Cos 8 3 O And P 2 8 P Find Ea Chegg Com



Value Of Tan Pi 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange



Cos Pi 3 Sin Pi 2 Find The Exact Value Youtube


The Trigonometric Ratios Of Angl
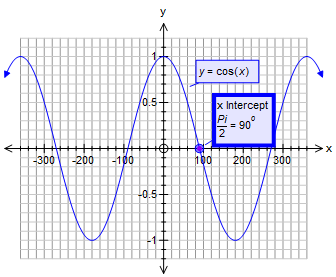


How Do You Find The Value Of Cos Pi 2 Using The Graph Socratic
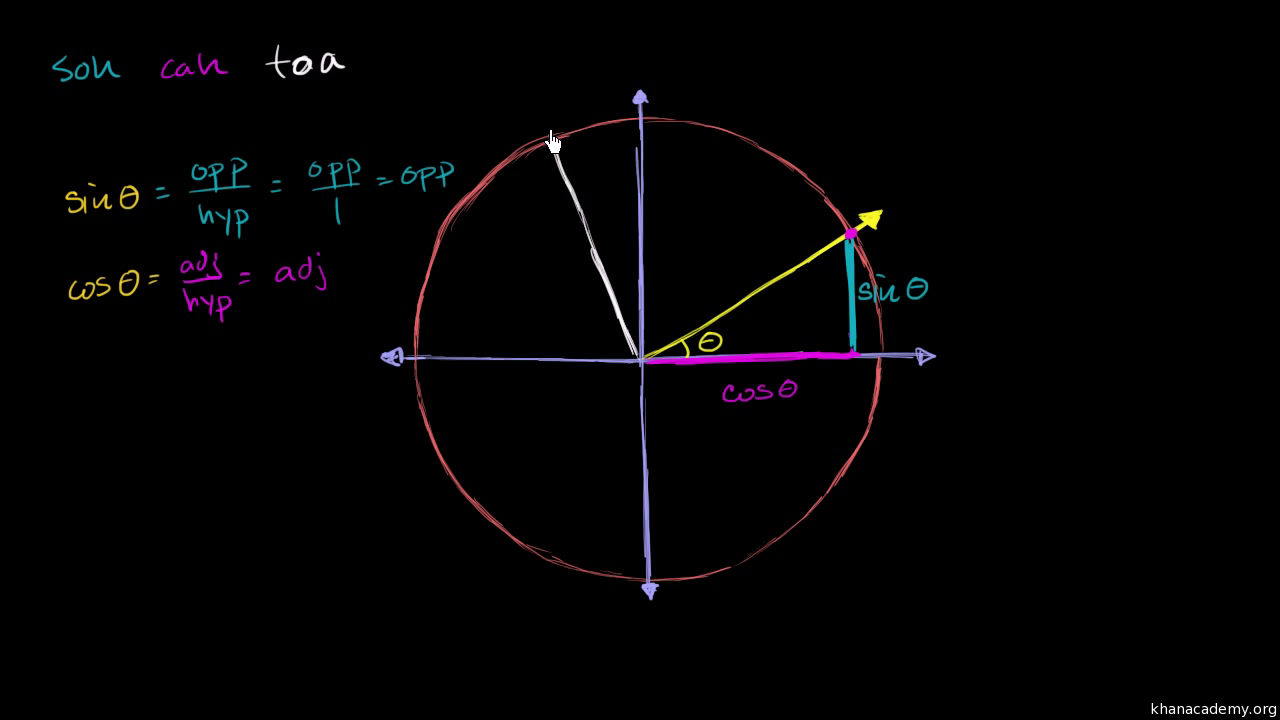


Sine Cosine Identities Periodicity Video Khan Academy


Biomath Trigonometric Functions


How To Find The Sin Pi 2 Value Using A Scientific Calculator Quora
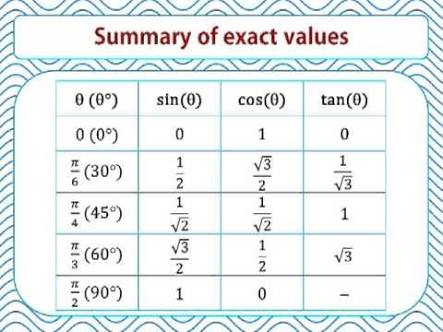


How Do You Find The Value Of Cos Pi 4 Socratic


Graphs Of The Sine And Cosine Function Precalculus Ii
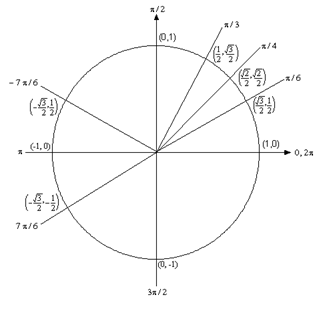


Algebra Trig Review



3pi 52 Remise Www Muminlerotomotiv Com Tr
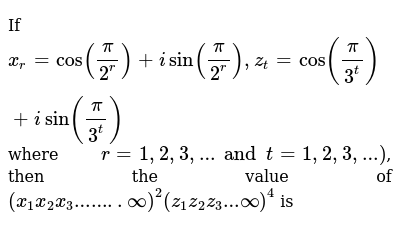


If X R Cos Pi 2 R I Sin Pi 2 R Z T Cos Pi 3 T I Si
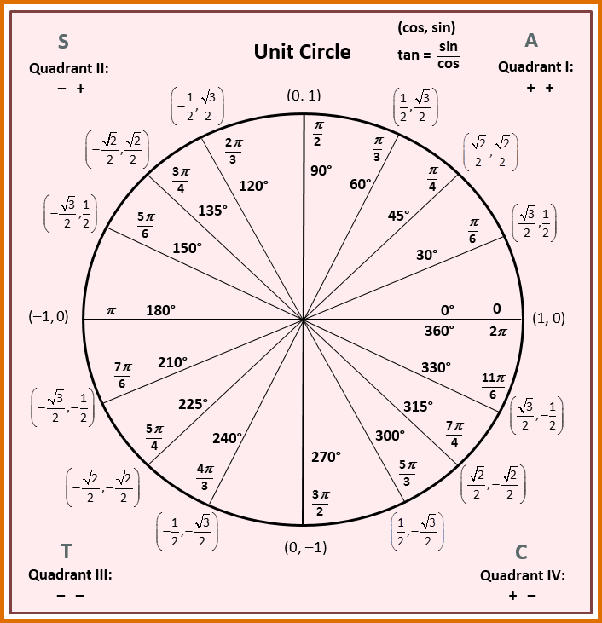


How Do You Find The Exact Value Of Cos P 3 Socratic



Show The Trig Identity Sin Pi 2 Theta Cos Theta Youtube



Sines And Cosines For Fractions Of P



The Value Of Cos Y Cos P 2 X Cos P 2 Y Cos X Sin Ycos P 2 X Cosxsin P 2 Y Is Zero If Brainly In



Solved Find The Exact Value Of Cos Pi 12 By Using Pi 12 Chegg Com


Find The Value Of Cos P 6 Cos 1 1 2 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


Solved Prove The Following Cos Pi 2 X Sin Tanxsin2x 2sin 2 X Find The Exact Value Using The Unit Circle For Tan 5pi 3 Determine The Exact Valu Course Hero



The Value Of Cos P 2 Cos P 2 Cos P 2 Sin P 2 Is A 1 512 B 1 1024 C Brainly In


Why Is 2 Cos P 5 F Quora



Trigonometry Angles Pi 2 From Wolfram Mathworld
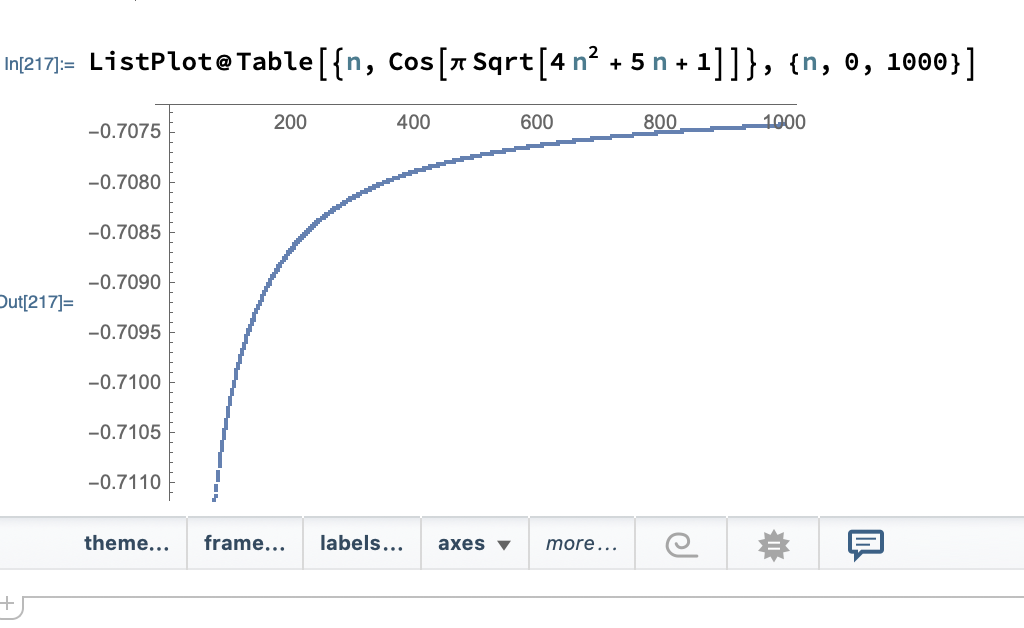


Computing The Limit Lim N To Infty Cos Left Pi Sqrt 4n 2 5n 1 Right For N In b Z Mathematica Stack Exchange



Find The Value Of Cos Cos 1 Sqrt2 2 Pi 2 A 2 B Sqrt2 C 2 X Sqrt2 D Sqrt2 2 Brainly Com


Graph Sine And Cosine Functions
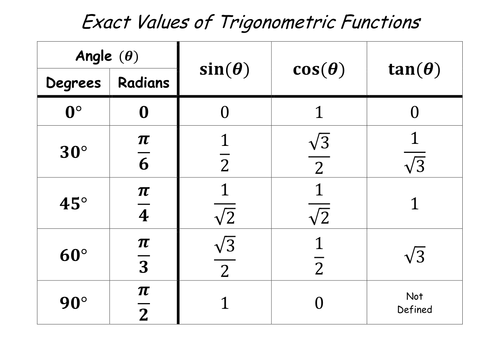


How Do You Evaluate 2 Cos Pi 3 6 Tan Pi 3 Socratic
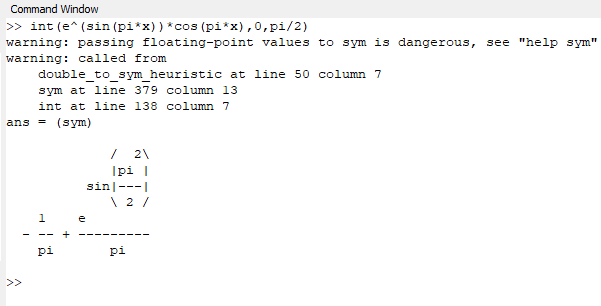


0 P 2 E Sin P X Cos P X Dx Homework Help And Answers Slader


Calculated Cos Pi 2 With My Graphing Calculator It Says 5 e 12 Instead Of 0 Why Quora



How To Solve Cos Pi 2 T Ge 0 Mathematics Stack Exchange



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿